Amateur Fossil Hunter Discovers New ‘Sea Dragon’ Species on British Beach
A two-meter-long fossil of a new type of prehistoric “sea dragon” has been discovered on a Dorset beach.
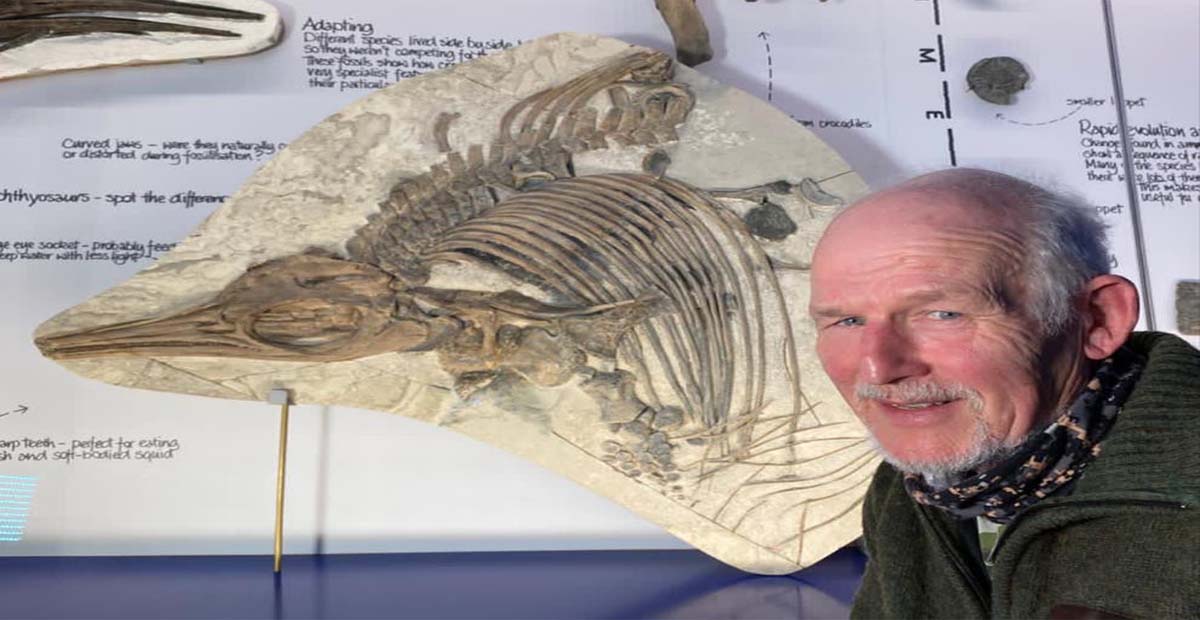
Amateur fossil hunter Dr. Steve Etches found the ichthyosaur fossil buried head-first in limestone.
The new type of creature has been called Etches sea dragon after Dr. Etches. They are called sea dragons because of their very large teeth and eyes.
Dr. Etches thought the teeth were unusual, so he passed it on to experts at the University of Portsmouth, where master’s student Megan Jacobs, who has spent several years working on ichthyosaurs, identified it as a new genus and species which lived 150 million years ago.
Researchers say the discovery is the UK’s fifth known ichthyosaur from the Late Jurassic period and by far the smallest so far.
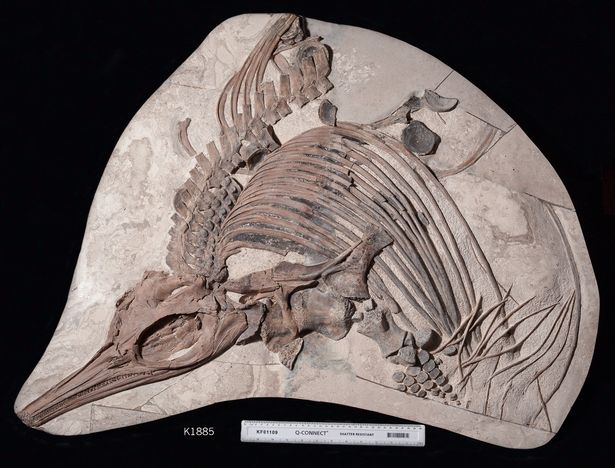
The fossil was found near Kimmeridge Bay – part of the Jurassic Coast World Heritage Site – in a limestone known as the white stone band.
When the ichthyosaur died, the seafloor would have been a very soft ooze, allowing the front half of the animal to sink into the mud before scavengers came along and ate the tail end.
As a result of being buried in this way, it was preserved in exceptional conditions and even some of its soft tissues were preserved.
Ms. Jacobs said: “Skeletons of Late Jurassic ichthyosaurs in the UK are extremely rare, so, after doing some research, comparing it with those known from other Late Jurassic deposits around the world and not being able to find a match was very exciting.
“Thalassodraco etches is a beautifully preserved ichthyosaur, with soft tissue preservation making it all the more interesting.
“Steve’s incredible collection contains many new and exciting animals and being given the chance to describe this ichthyosaur was a real privilege.”
Ichthyosaurs were highly adapted marine predators, with a streamlined bodies for gliding through the water, large eyes for enhanced vision, and elongated jaws full of conical teeth, well-suited for catching slippery fish and squid.
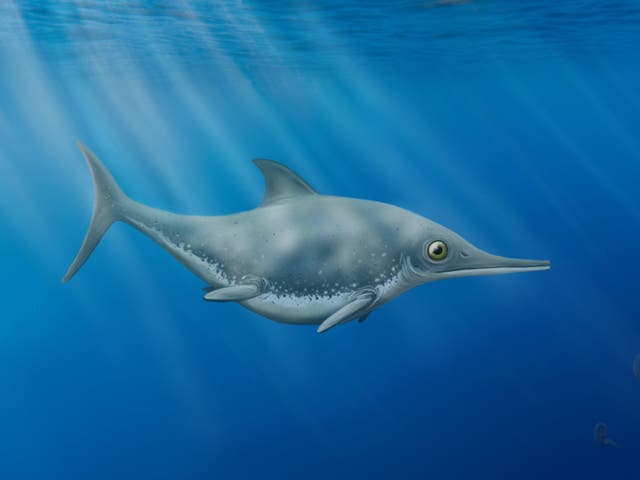

The newly discovered species has a deep ribcage, small forelimbs and hundreds of tiny, delicate, smooth teeth.
The specimen is on display alongside Dr. Etches’s other many fossils in his museum in Dorset, the Etches Collection, which he built to house the many discoveries he’s made over a lifetime of fossil hunting.
Dr. Etches said: “I’m very pleased that this ichthyosaur has been found to be new to science, and I’m very honored for it to be named after me.
“It’s excellent that new species of ichthyosaurs are still being discovered – which shows just how diverse these incredible animals were in the Late Jurassic seas.”
The research is published in the online journal PLOS One.